Maintaining a healthy aquarium environment hinges on regular water changes, and siphoning is the key. This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to effectively and safely siphon aquarium water, ensuring optimal conditions for your aquatic inhabitants. Learn the essential techniques, from setting up the siphon to handling waste, to ensure a thriving ecosystem.
Proper siphoning removes accumulated debris, nitrates, and other waste products, preventing the buildup of harmful toxins. This crucial maintenance task promotes the health and well-being of your fish, invertebrates, and plants, contributing to a vibrant and balanced aquarium.
Introduction to Siphoning Aquarium Water
Siphoning aquarium water is a crucial part of maintaining a healthy and thriving aquatic environment. This process removes excess water, debris, and waste products, preventing the buildup of harmful substances that can negatively impact fish and plant health. Proper siphoning is essential for maintaining water quality, promoting a balanced ecosystem, and preventing potential disease outbreaks.
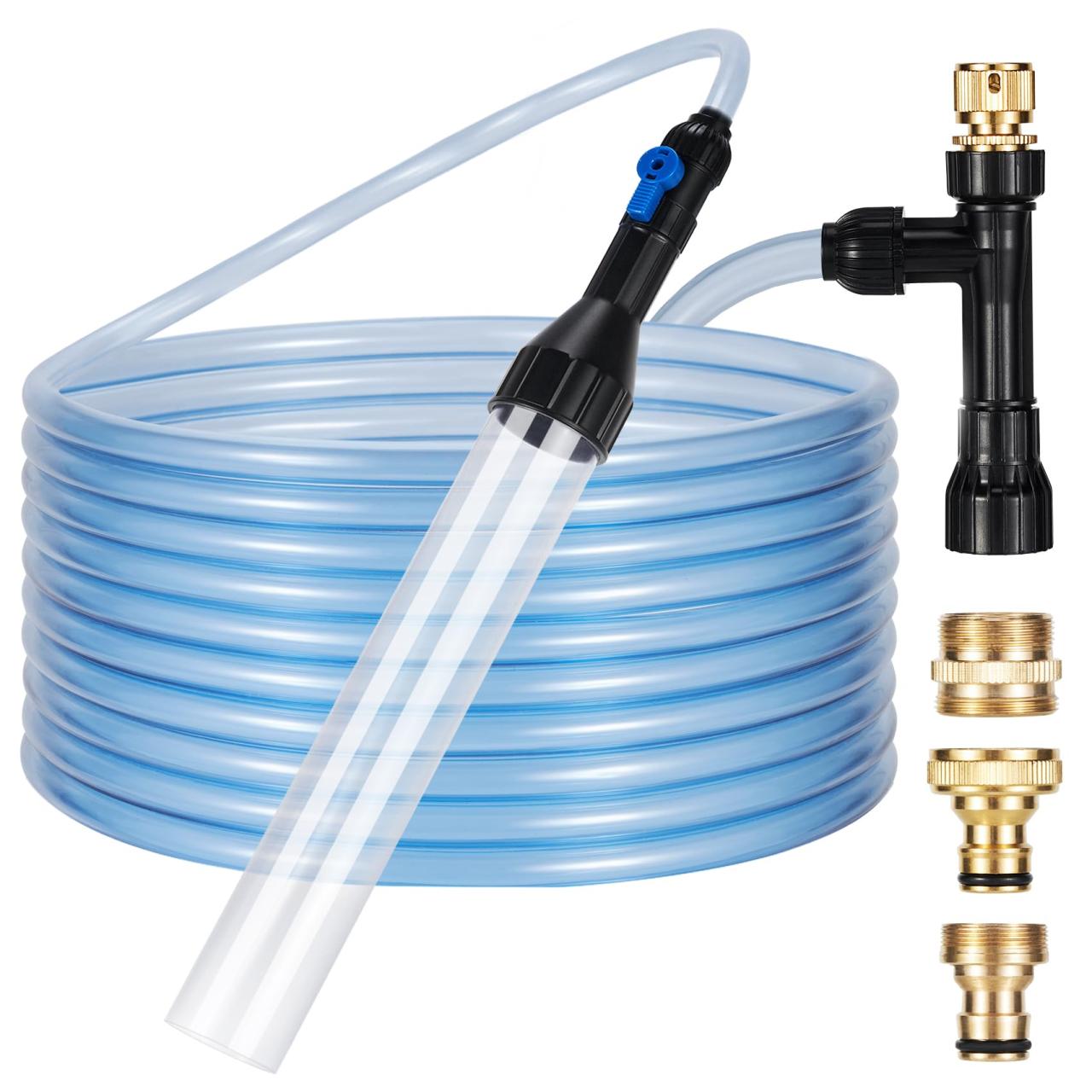
Essential Tools and Materials
Effective siphoning relies on the correct tools and materials. This ensures a smooth and efficient process, minimizing disruption to the aquarium ecosystem. The following tools are vital for successful water siphoning.
| Tool | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Siphon tube | A flexible tube, typically made of plastic or rubber, with a narrow opening at one end. | Used to transport water from the aquarium. |
| Bucket or container | A receptacle for collecting the water being siphoned. | Provides a designated area for draining aquarium water. |
| Handheld siphoning pump | A small pump that creates suction to accelerate the siphoning process. | Increases the flow rate of water removal, reducing the time needed for siphoning. |
| Gravel vacuum | A specialized tool with a narrow nozzle and a flexible tube. | Effectively removes debris and waste from the gravel bed without disturbing the substrate significantly. |
| Small, flat-bladed spatula or scraper | A small, flat-bladed tool for removing debris that might clog the siphon tube. | Useful for cleaning the siphon tube and removing large particles that could impede the siphoning process. |
Significance of Proper Water Siphoning
Proper siphoning is vital for maintaining a healthy aquarium environment. Regular siphoning removes uneaten food, fish waste, and decaying plant matter, preventing ammonia and nitrite spikes. These harmful compounds can lead to significant health problems for the fish, ultimately causing stress, disease, and even death. By consistently removing these contaminants, you help maintain a stable and healthy water chemistry, fostering a thriving ecosystem for your aquatic inhabitants.
This preventative measure ensures the well-being of your aquarium community and promotes optimal growth and longevity.
Setting Up the Siphon
Properly setting up the siphon is crucial for efficient and safe aquarium water removal. A correctly positioned and connected siphon ensures minimal disruption to the aquarium ecosystem and allows for controlled water transfer. This section details the steps involved in establishing a functional siphon system.
Preparing the Siphon Tube
The siphon tube, a crucial component of the water removal process, needs careful preparation before deployment. Ensure the tube is free of obstructions and debris that could hinder the flow of water. Inspect the tube for any cracks or damage that could compromise its integrity. These factors influence the efficacy of the water transfer process and prevent unwanted incidents.
Positioning the Siphon Tube in the Aquarium
Positioning the siphon tube within the aquarium is vital for successful water removal. The tube’s placement dictates the volume and rate of water extraction. The lower end of the tube should be immersed in the aquarium water at the desired extraction point. Avoid placing the tube near or over delicate plants, fish, or decorations to prevent disturbance.
Connecting the Tube to the Output Point
Connecting the siphon tube to the desired output point is the final preparatory step. This step ensures smooth water transfer from the aquarium to the destination. The upper end of the siphon tube should be positioned above the water level in the aquarium. This setup creates the necessary pressure difference for efficient water flow.
Step-by-Step Setup Instructions
- Inspect the siphon tube for any damage or obstructions. Clean the tube thoroughly to ensure a clear path for water flow.
- Submerge the lower end of the siphon tube into the aquarium water at the desired extraction point. Consider the position of the tube to avoid disturbing fish or decorations.
- Position the upper end of the siphon tube above the water level of the aquarium. This creates the pressure difference necessary for water flow.
- Securely connect the siphon tube to the output point. Ensure a tight connection to prevent leaks or backflow.
- Begin siphoning the water once the setup is complete. Monitor the flow rate and adjust the position of the tube as needed.
Siphoning Procedures
Proper siphoning is crucial for maintaining a healthy aquarium environment. It allows you to remove excess water, potentially contaminated with uneaten food, waste products, and accumulated debris, while minimizing disturbance to the delicate ecosystem within the tank. Careful siphoning techniques ensure the well-being of your fish and other aquatic inhabitants, as well as the longevity of your aquarium’s overall health.
Safe and Efficient Siphoning Steps
The following steps detail a safe and efficient siphoning procedure. Adhering to these steps will help maintain a healthy aquarium environment.
- Prepare the necessary tools. This includes the siphon hose, bucket, gravel vacuum (optional), and any necessary clamps or connectors. Ensure the tools are clean and appropriate for the size of your aquarium. This step is essential for a smooth and effective siphoning process.
- Position the bucket or container below the aquarium. This ensures the siphoned water flows directly to the collection vessel. A bucket or a container with a sufficient volume to hold the water to be removed is essential. Ensure the container is positioned at a suitable level to allow the water to flow smoothly and avoid any overflow.
- Submerge the siphon hose’s end in the aquarium water, just a few inches above the substrate. Submerging the hose is critical to creating the suction necessary for the siphoning process. This step ensures that water flows into the hose smoothly, without air getting in. Avoid placing the hose directly on the gravel or substrate to prevent excessive disturbance.
- Place the other end of the siphon hose in the designated collection container. This allows the water to flow from the aquarium to the collection container, enabling you to remove the water. Ensure the siphon hose is submerged to avoid air pockets, ensuring a smooth flow of water.
- Start the siphoning process by creating suction. This typically involves pulling the siphon hose up and out of the water or using a vacuum source. The suction should be maintained to ensure that the water flows smoothly and continuously.
- Slowly and carefully adjust the siphon to control the water flow. A steady and controlled flow rate is preferable to avoid disturbing the substrate or aquarium inhabitants. A rapid flow can cause significant disruption to the substrate and the inhabitants. This step ensures that the water is removed without causing any unnecessary stress or disturbance to the environment.
- Continue the siphoning process until the desired amount of water has been removed. Monitor the water level regularly to prevent over-siphoning or under-siphoning. Regular monitoring of the water level prevents any mishaps and maintains the desired water level.
- Once the siphoning is complete, carefully remove the siphon hose from the aquarium and the container. Properly storing or cleaning the tools is important for future use.
Controlling Water Flow Rate
Controlling the flow rate is vital to minimize disruption. Several factors influence the flow rate, including the siphon’s diameter, the length of the hose, and the height difference between the aquarium and collection container.
- Adjust the suction level. Increasing suction typically increases the flow rate. Adjusting the suction level allows for a controlled flow rate, minimizing disturbances to the substrate and inhabitants.
- Vary the height difference. A greater height difference between the aquarium and collection container usually results in a faster flow rate. The height difference affects the flow rate, and adjustments are necessary for optimal results.
- Use a gravel vacuum for localized siphoning. Gravel vacuums are beneficial for removing debris and waste from specific areas without disturbing the entire substrate. Using a gravel vacuum allows for localized cleaning, minimizing the impact on the surrounding environment.
Avoiding Substrate and Inhabitants Disturbance
Careful handling of the siphon hose is crucial to minimize disturbance. Use the siphon gently, ensuring the hose isn’t dragged across the substrate or fish are not disturbed.
- Maintain a slow and steady flow rate to minimize disturbance. A controlled flow rate prevents disruption to the substrate and inhabitants, allowing for a smooth siphoning process.
- Avoid forcefully pulling the siphon hose. Sudden movements or forceful pulling of the siphon hose can stir up sediment and disturb fish or other aquatic inhabitants.
- Use a gravel vacuum for localized cleaning when necessary. This helps to minimize disturbance and enables precise cleaning of specific areas of the substrate. This ensures that only the necessary areas are cleaned, and the environment is maintained.
Comparing Siphoning Techniques
Different techniques offer various advantages and disadvantages.
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Siphoning with a bucket | Simple and affordable | Can disturb the substrate and inhabitants more easily |
| Siphoning with a gravel vacuum | Precise localized cleaning, less disturbance | More expensive, may not be suitable for all aquariums |
Handling Waste and Debris

Properly managing the collected water and debris is crucial for maintaining a healthy aquarium environment and preventing the spread of diseases. Careful disposal procedures minimize the risk of contaminating the aquarium and ensure the well-being of your aquatic inhabitants.Effective waste management involves understanding how to safely dispose of the collected water and debris, preventing the transmission of diseases, and properly cleaning the siphon tube to maintain hygiene.
This section Artikels the essential steps for responsible handling of waste.
Disposal of Collected Water
The collected water, often containing waste products and potentially harmful substances, needs careful consideration for disposal. Simply pouring it down the drain can lead to introducing pollutants into the sewage system.
- Safe Water Disposal: Pour the collected water into a designated container, separate from the aquarium. Avoid dumping it directly into sinks, toilets, or drains, as it can introduce harmful substances into the water supply. For example, excess nitrates or phosphates from the aquarium can disrupt the natural balance in local waterways if discharged directly into the environment. A bucket or similar container will work for temporary storage.
- Additional Precautions: If you suspect the water contains chemicals or other harmful substances, consult with local authorities regarding the appropriate disposal methods. Ensure your disposal method adheres to local regulations.
Disposal of Debris and Solids
The collected solid debris, such as uneaten food, dead plants, and waste from fish, needs careful disposal.
- Waste Container: Use a separate, sealed container for the debris. Avoid mixing the debris with other household waste.
- Proper Disposal: Dispose of the sealed container with other household garbage. This method prevents the spread of diseases and keeps the environment clean.
Disease Prevention
Contaminated water can introduce diseases to the aquarium. Following proper procedures during siphoning helps mitigate this risk.
- Preventative Measures: Use a separate container for the collected water and debris to prevent contamination of the aquarium water. Isolate any visibly sick fish immediately. Maintaining proper water quality parameters, like temperature and pH, minimizes the risk of disease.
- Disease Prevention Tips: Avoid using the same siphon tube for both siphoning and water changes. Always clean the tube thoroughly before and after use. Use fresh water to rinse the collected water and debris container. This prevents disease transmission.
Cleaning the Siphon Tube
Proper cleaning of the siphon tube is essential to maintain hygiene and prevent the spread of diseases.
- Cleaning Procedure: Rinse the siphon tube thoroughly with water after each use. A solution of mild dish soap can be used for a more thorough cleaning, followed by a final rinse with clean water. Avoid using harsh chemicals that can damage the tube or harm the aquarium inhabitants. Avoid using abrasive materials that could scratch the tube and cause damage.
- Drying: Allow the tube to dry completely before storing it. This prevents the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms that can contaminate the aquarium.
Safe Disposal Procedure
The procedure for safe aquarium waste disposal involves several key steps for responsible waste management.
- Collection: Collect the waste water and debris in a separate container. This container should be labeled to indicate the contents.
- Segregation: Segregate the collected waste water from the debris. This will facilitate separate disposal procedures for each type of waste.
- Disposal: Dispose of the waste water according to local regulations and guidelines. For example, in some areas, water from aquariums containing fish may need specific handling to prevent the introduction of invasive species. Contact your local waste management office for specific instructions.
Safety Considerations During Siphoning
Proper siphoning of aquarium water is crucial for maintaining a healthy aquatic environment. However, careful attention to safety precautions is paramount to avoid accidents and ensure the well-being of both the aquarium inhabitants and the siphoning personnel. Neglecting safety measures can lead to injury, damage to equipment, and stress for the fish.Accidents during siphoning, while often preventable, can occur.
Understanding potential hazards and implementing appropriate safety measures minimizes the risk of these incidents. This section Artikels essential safety precautions for a safe and successful siphoning process.
Potential Hazards and Risks
The siphoning process, while generally safe, presents several potential hazards. These include slips, trips, and falls due to wet surfaces, especially when dealing with water-filled containers or tubs. Improper handling of the siphon tube can lead to cuts or abrasions. The suction force generated by the siphon can be significant and potentially hazardous if not handled correctly.
Furthermore, the possibility of splashing or spills of water can lead to accidental submersion or contact with electrical equipment. Understanding these risks is crucial for implementing preventative measures.
Preventing Accidents During Siphoning
To mitigate the risks associated with siphoning, a proactive approach is essential. Ensure the area where siphoning is taking place is well-lit and free of obstructions. Wear appropriate footwear to maintain stability and prevent slips. Inspect the siphon tube and equipment for any cracks, leaks, or damage before use. Use caution when manipulating the siphon tube, avoiding forceful movements that could lead to breakage or injury.
Have a bucket or container ready to catch the siphoned water, and use a secondary container to catch waste to minimize the risk of spills. Ensure electrical outlets and appliances are not located near the siphoning area to prevent accidental contact with water.
Safe Handling of Siphon Tube and Equipment
Proper handling of the siphon tube and associated equipment is crucial to prevent accidents. When inserting the siphon tube into the aquarium, do so slowly and gently to avoid startling or injuring the fish. Avoid forceful insertions or rapid movements, which can dislodge or damage aquarium decorations or harm aquatic life. Handle the siphon tube with care, avoiding sharp or abrasive surfaces.
If the siphon tube becomes entangled or obstructed, do not force it. Instead, carefully dislodge the obstruction. Always ensure the siphon tube is securely attached to the container to avoid accidental detachment and spillage. Ensure that all equipment is properly secured and stable to prevent any tipping or toppling. Regular inspection of the equipment for damage before use is vital to maintaining a safe work environment.
Waste Disposal and Debris Handling
Disposing of siphoned water and debris properly is a crucial part of the process. Use appropriate containers for waste disposal and ensure that they are not overflowing or leaking. Avoid disposing of waste in areas that could cause harm to the environment. If the waste contains harmful materials, dispose of it according to local regulations. Proper waste management practices minimize the risks associated with siphoning and protect the environment.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

Siphoning aquarium water, while generally straightforward, can sometimes present challenges. Understanding potential problems and their solutions is crucial for maintaining a healthy aquarium environment. This section Artikels common issues encountered during siphoning and provides effective solutions.Effective siphoning relies on a consistent and controlled flow of water. Interruptions or blockages can significantly impact the efficiency of the process.
Different aquarium setups, from those with complex filtration systems to those with intricate gravel beds, may present unique challenges. Careful attention to these potential issues will ensure a smooth and successful water change.
Flow Rate Issues
Maintaining a consistent water flow is essential for efficient siphoning. Several factors can affect the flow rate. A decrease in flow could be due to a blockage within the siphon tube or a mismatch between the tube’s diameter and the volume of water being siphoned. Conversely, an excessively high flow rate might cause excessive turbulence, leading to disruption of the aquarium environment.
A well-adjusted flow rate ensures a smooth and controlled water change.
Siphon Tube Blockages
Blockages in the siphon tube are a common occurrence during siphoning. These blockages can be caused by various debris, including uneaten food, dead plant matter, or small gravel particles. These obstructions hinder the water’s flow, reducing the effectiveness of the siphon. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the siphon tube can prevent these blockages.
Siphoning Problems in Specific Aquarium Setups
Different aquarium setups can present unique siphoning challenges. For example, aquariums with intricate gravel beds or dense plant growth may require a more gentle approach to avoid disturbing the substrate or damaging delicate plants. Conversely, aquariums with strong filtration systems might require adjustments to the siphon’s positioning to avoid interfering with the filter’s operation.
Troubleshooting Specific Issues
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Slow or no flow | Clogged siphon tube, kinked tube, incorrect tube diameter, low water level in the source tank | Clear the tube, straighten the tube, use a wider tube if needed, ensure a sufficient water level in the source tank. |
| Water splashing/turbulence | Excessive flow rate, improper tube positioning, air entering the siphon | Adjust the siphon’s position to reduce the flow rate, use a narrower tube if necessary, ensure the tube is submerged. |
| Debris getting stuck in the siphon tube | Uneaten food, gravel, or other particles clogging the tube | Regularly clean the siphon tube, consider using a fine mesh strainer to filter out debris before it enters the tube. |
Implementing these troubleshooting strategies can help overcome common siphoning challenges, ensuring a smooth and efficient water change process in your aquarium.
Advanced Siphoning Techniques
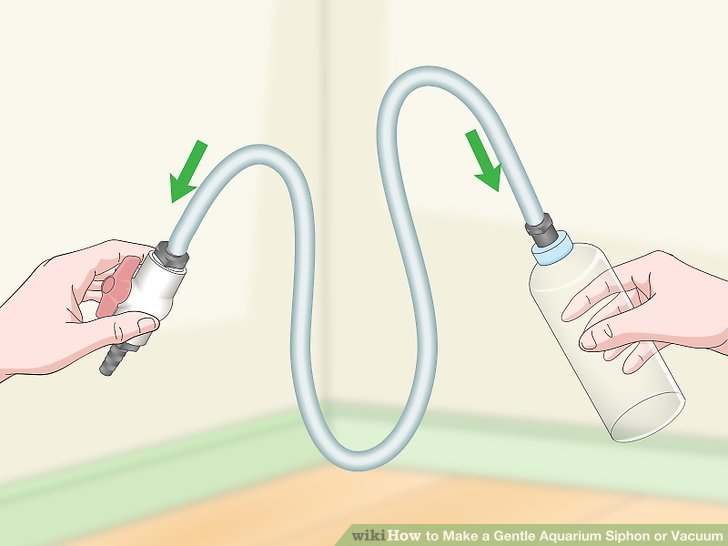
Mastering the art of siphoning goes beyond basic procedures. Advanced techniques allow for more precise and targeted water changes, minimizing disruption to your aquarium’s delicate ecosystem. This section explores specialized methods tailored to specific needs and tank sizes, providing you with the tools to maintain optimal water quality.
Specialized Siphoning Methods for Specific Debris
Different types of debris require tailored approaches for effective removal. A simple siphon may not always be sufficient for fine particles, algae, or uneaten food. Specialized techniques provide a targeted approach to maintain water clarity and prevent future buildup.
- Removing Fine Particles: For stubborn cloudiness or suspended particles, consider using a fine-mesh net or a specialized filter sock fitted to the siphon tube. This traps fine particles that might otherwise remain in the water column. A fine-mesh sock can be placed inside the siphon tube to help remove these particles. This method proves particularly useful for tanks with gravel substrates.
- Removing Algae: If algae buildup is a concern, a combination of siphoning and algae scrapers or specialized algae removal tools might be necessary. Manual removal of algae from the glass or substrate is often a part of this process. Using a siphon with a narrow opening can allow for targeted removal of algae from specific areas of the tank.
- Removing Uneaten Food: Siphoning in conjunction with regular feeding schedules and careful monitoring is key to prevent uneaten food from decomposing and clouding the water. Quickly removing uneaten food minimizes the chance of bacterial blooms.
Comparing Siphoning Techniques for Different Tank Sizes
The size of your aquarium dictates the most effective siphoning method. Larger tanks require more substantial equipment and more time. Smaller tanks are more easily handled and cleaned with a basic setup.
| Tank Size | Siphoning Technique | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Small (under 10 gallons) | Basic siphon with a shorter tube and a gentle suction. | Requires less effort, easy to manage. |
| Medium (10-30 gallons) | A standard siphon with a longer tube. | More time is needed for water changes. |
| Large (over 30 gallons) | A powerful siphon, potentially with multiple siphoning points for efficiency. | Efficiency is paramount for large tanks. Consider using multiple siphons to accelerate the process. |
Cleaning the Siphon After Use
Thorough cleaning of the siphon after each use is crucial for maintaining its functionality and preventing the buildup of debris.
- Disassembly: Carefully disassemble the siphon, separating all components.
- Rinsing: Rinse all parts thoroughly under running water, removing any visible debris.
- Soaking: For stubborn residues, consider soaking the siphon components in a mild aquarium cleaner solution. Be sure to thoroughly rinse with clean water afterwards.
- Drying: Allow all components to dry completely before storing the siphon to prevent mold and mildew growth.
Examples of Specialized Siphoning Techniques
Certain situations demand specialized siphoning techniques to address specific needs.
- Removing a significant amount of waste after a large fish feeding: A more powerful siphon or a multiple-point siphon setup may be required to remove excess uneaten food efficiently and prevent water quality degradation.
- Cleaning a tank with a heavily planted substrate: A gentler approach, using a siphon with a narrow tube, may be necessary to avoid disturbing the delicate plant roots and substrate. Use a fine-mesh filter sock to minimize disturbance.
Siphoning Different Aquarium Types
Siphoning aquarium water is a crucial maintenance task, but the specific approach varies significantly depending on the type of aquarium. Different tank setups present unique challenges and opportunities that require tailored techniques. Understanding these variations ensures effective water changes without disrupting the delicate balance of the ecosystem within each aquarium.Careful consideration of tank features, including the presence of plants, corals, and other inhabitants, is essential to prevent damage and maintain the overall health of the aquarium.
A well-executed siphoning procedure minimizes stress on the aquatic life and preserves the intricate biological balance within the aquarium.
Planted Aquariums
Planted aquariums often contain intricate root systems and dense plant growth. Carefully positioning the siphon is crucial to avoid damaging delicate roots and stems. A gentle approach, using a slower siphoning speed, is recommended to minimize the disturbance of the substrate. Using a flexible siphon tube can be advantageous in navigating around plants without causing stress.
Reef Aquariums
Reef aquariums present unique challenges due to the presence of corals and other invertebrates. The delicate nature of corals requires utmost care during siphoning. Avoid strong water currents, which can dislodge or harm corals. Using a gentle siphon and minimizing the disturbance to the substrate is vital to prevent coral damage. A slow and steady approach is key to a successful siphoning procedure in a reef tank.
Aquariums with Intricate Designs or Features
Intricate tank designs, including caves, rockscapes, and hidden areas, require specialized siphoning techniques. A flexible siphon tube allows for maneuvering around these features. Thorough inspection of the tank’s layout before beginning the siphoning process ensures that no debris or organisms are trapped in the intricate features. Carefully guide the siphon to avoid damaging or displacing decorative elements.
Maintaining Biological Filtration
The biological filtration system is a vital component of any aquarium. Siphoning should be conducted in a way that minimizes disturbance to this system. Avoid siphoning water from areas directly over the filter media or from the filter intake. Allow the filter to remain in place during the siphoning process, maintaining the biological filtration cycle.
Illustrative Examples

Siphoning aquarium water is a crucial maintenance task, and understanding various scenarios can greatly enhance your success. These examples illustrate the process in diverse aquarium setups, providing practical guidance for effective and safe water changes. Different aquarium types and features require specific techniques, and these examples highlight these nuances.
Siphoning a Standard Tank
This scenario describes the basic siphoning process for a typical rectangular aquarium without special features. 
Image Description: A rectangular aquarium is depicted. A siphon tube is submerged in the aquarium water near the back. The other end of the tube is placed into a container outside the tank. The siphon is positioned to collect water from the deeper parts of the tank. The image visually demonstrates the water level gradually lowering in the aquarium.
- Submerge the siphon tube’s end into the aquarium water, ensuring it’s positioned to collect water from the deeper parts of the tank. This prevents trapping air bubbles, which can hinder the siphoning process.
- Position the other end of the siphon tube into the appropriate collection container. Ensure the container is below the water level in the tank to facilitate the flow.
- Create a vacuum by slightly raising the container to initiate water flow through the tube. The water level in the aquarium will begin to decrease.
- Maintain a steady flow by adjusting the position of the container or tube as needed. The rate of water change will depend on the siphon’s size and the diameter of the tube. For example, a larger diameter tube will move water faster than a smaller one.
- Once the desired water level is reached, carefully lift the siphon tube out of the aquarium, ensuring no water spills back into the tank. Disconnecting the tube slowly avoids splashing and prevents disturbing the aquarium inhabitants.
Siphoning a Tank with a Waterfall Feature
Waterfall aquariums present unique challenges. Careful planning and precise technique are crucial. 
Image Description: An aquarium with a waterfall feature is illustrated. The siphon tube is placed at the bottom of the waterfall area, avoiding the flow of water from the waterfall. The water is collected in a separate container. The image highlights the placement of the siphon to capture water without disrupting the waterfall’s aesthetic.
- Position the siphon tube carefully at the base of the waterfall, avoiding direct contact with the flowing water. This prevents interruption of the waterfall’s operation.
- Ensure the siphon tube’s opening is not positioned in a way that blocks the waterfall’s flow. This ensures that the water from the waterfall is not redirected, and the waterfall remains functioning as intended.
- The siphon should be positioned to collect water that drains from the waterfall rather than the water directly falling from the top of the waterfall. This ensures the siphoning process does not disturb the flow of water through the waterfall’s design.
- Use a separate container to collect the water being siphoned from the waterfall. This allows the waterfall to continue functioning without interfering with the water change process.
Siphoning a Tank with an External Filter
External filter systems require a specialized approach. 
Image Description: An aquarium with an external filter is shown. The siphon tube is positioned at the base of the aquarium, below the intake of the external filter, and extends to a collection container. The image shows how the siphon avoids the filter intake area to maintain filter functionality.
- Carefully position the siphon tube below the water level of the aquarium, but above the intake of the external filter system. This ensures the filter is not affected by the siphoning process.
- Ensure the siphon tube is not placed near or in contact with the filter intake, maintaining the function of the filter.
- Use a separate container to collect the water being siphoned from the aquarium, keeping the filter system’s operation undisturbed.
Closure
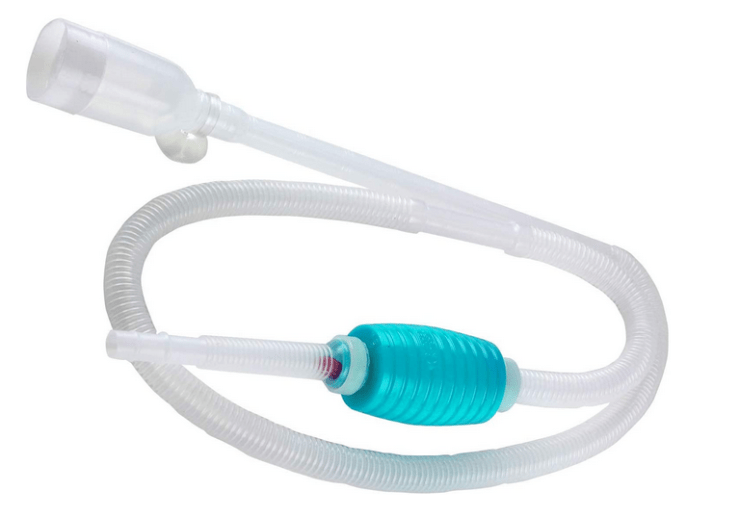
In conclusion, siphoning aquarium water is a vital aspect of aquarium maintenance. By following the detailed procedures Artikeld in this guide, you can effectively remove waste, maintain water quality, and ensure the long-term health of your aquatic community. Whether you’re a seasoned aquarist or a beginner, this guide equips you with the knowledge and skills necessary to perform this task with confidence and precision.