Swim bladder disorder is a common ailment affecting various fish species, often stemming from a combination of factors. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial for successful recovery. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of understanding, diagnosing, and treating swim bladder disorder in fish, offering practical advice and solutions for aquarium enthusiasts.
From understanding the different types of swim bladder disorders and their underlying causes to detailed diagnostic procedures and effective treatment methods, this guide provides a structured approach. Environmental considerations, nutritional support, and long-term care are also explored, equipping you with the knowledge needed to help your fish thrive.
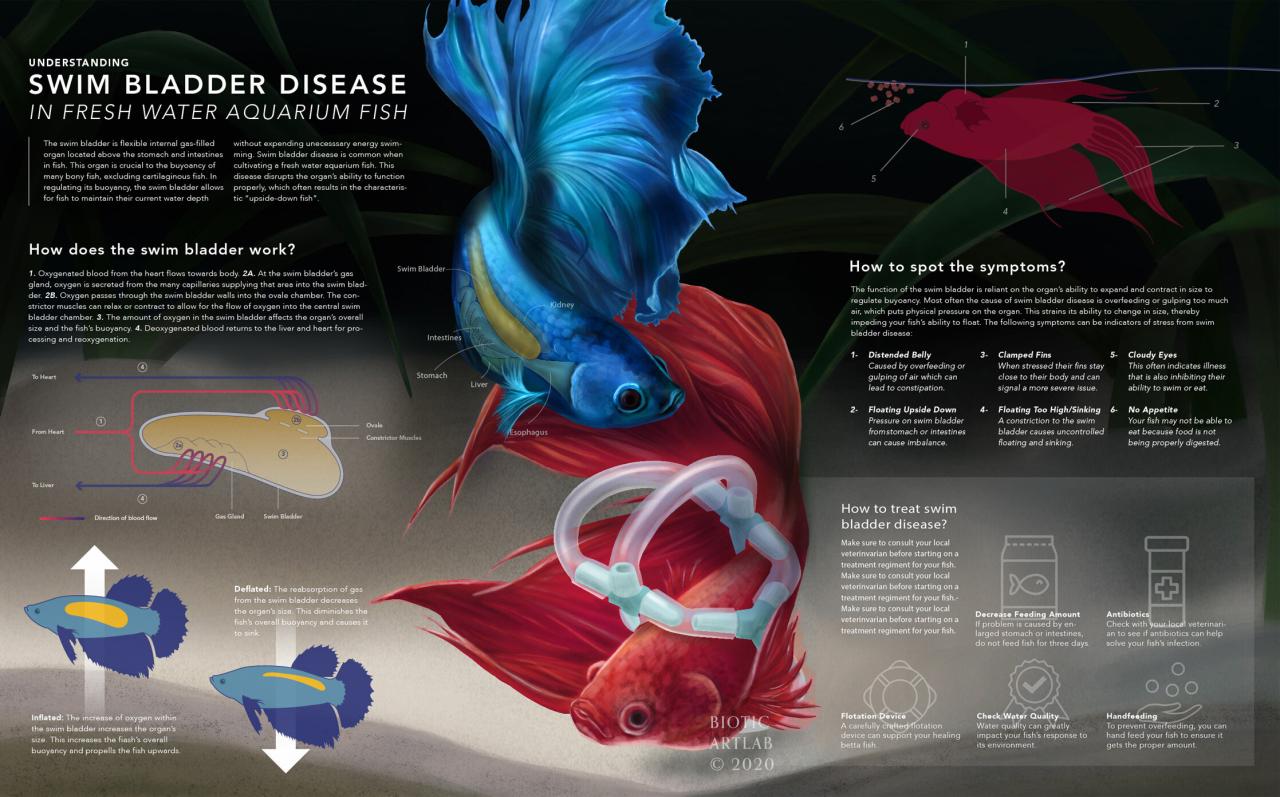
Understanding Swim Bladder Disorder

Swim bladder disorder, a common ailment affecting various fish species, significantly impacts their buoyancy and overall well-being. Understanding the different types, causes, and symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment. Proper identification of the issue can often lead to successful recovery.Swim bladder disorders encompass a range of conditions affecting the swim bladder’s function. The swim bladder is an air-filled organ that helps fish maintain neutral buoyancy, allowing them to stay at specific water depths without expending excessive energy.
Dysfunction of this organ can lead to a variety of problems, including difficulty swimming, erratic swimming patterns, and even death if left untreated.
Definition of Swim Bladder Disorder
Swim bladder disorder is a condition affecting the swim bladder, a gas-filled organ that allows fish to control their buoyancy. This organ is essential for maintaining proper depth in the water column. Disorders can range from mild buoyancy issues to severe complications, impacting the fish’s ability to feed, swim, and reproduce.
Types of Swim Bladder Disorders
Swim bladder disorders can be broadly classified into two primary types: infectious and non-infectious. Infectious disorders often stem from bacterial or fungal infections, whereas non-infectious disorders typically result from physical trauma, improper water conditions, or nutritional deficiencies.
Causes of Swim Bladder Disorders
Non-infectious causes can include physical trauma from collisions or rough handling, poor water quality (especially ammonia spikes or nitrite levels), nutritional deficiencies (lack of essential vitamins and minerals), or even parasites. Infectious causes are often bacterial or fungal infections.
Common Fish Species Affected
Many fish species are susceptible to swim bladder disorders, with some more prone than others. Cichlids, goldfish, and various types of tropical fish are frequently affected. However, the specific susceptibility depends on factors such as water conditions, diet, and stress levels.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of swim bladder disorder is crucial for successful treatment. Prompt intervention can minimize the severity of the condition and improve the fish’s chances of recovery. Delayed diagnosis often leads to complications, making treatment more challenging and potentially resulting in the fish’s demise.
Table of Common Swim Bladder Disorders
| Fish Species | Common Symptoms | Potential Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Goldfish | Erratic swimming, floating at the surface, or sinking to the bottom, difficulty maintaining position | Poor water quality, nutritional deficiencies, physical trauma, bacterial infections |
| Cichlids | Difficulty maintaining depth, erratic swimming, inability to hold position, lethargy | Poor water quality, parasites, physical trauma, nutritional deficiencies, bacterial or fungal infections |
| Betta Fish | Sinking or floating erratically, difficulty swimming, reduced activity levels | Poor water quality, stress, nutritional deficiencies, bacterial infections, or physical injury |
| Rainbow Trout | Difficulty swimming, labored breathing, and lethargy, abnormal swimming patterns, and changes in body shape | Bacterial infections, poor water quality, physical injury, parasites, nutritional deficiencies |
Diagnosis and Assessment

Diagnosing swim bladder disorder in fish requires a systematic approach, combining observation, physical examination, and water quality analysis. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for implementing appropriate treatment and improving the fish’s chances of recovery. Early detection allows for timely intervention, preventing further complications and maximizing the fish’s well-being.Comprehensive assessment involves a multifaceted evaluation of the fish’s physical condition, swimming behavior, and the surrounding water parameters.
This multi-pronged approach helps differentiate swim bladder disorder from other potential ailments and guides treatment strategies. Accurate identification is essential for effective intervention, as various factors can influence a fish’s buoyancy and swimming.
Diagnostic Procedures for Identifying Swim Bladder Disorder
Various diagnostic procedures are used to identify swim bladder disorder. These procedures help to ascertain the cause of the problem and guide treatment choices. Careful observation and recording of the fish’s behavior are crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Importance of Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination of the fish is paramount in diagnosing swim bladder disorder. Inspecting the fish’s overall condition, including external features and any signs of stress or disease, can reveal crucial clues. Examine the fish’s body condition, scales, fins, and any lesions or abnormalities. Note any unusual posture, asymmetry, or signs of pain.
Role of Water Quality Testing
Water quality testing plays a vital role in diagnosing swim bladder disorder. Assessing water parameters like ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, pH, and temperature can help determine if environmental factors are contributing to the problem. Inadequate water quality can negatively impact fish health and lead to a range of issues, including swim bladder disorder. It is essential to ensure that the water parameters are within the acceptable range for the species of fish being kept.
Evaluating Fish Buoyancy and Swimming Ability
Assessing a fish’s buoyancy and swimming ability is essential in diagnosing swim bladder disorder. Observe how the fish swims; does it swim erratically or in an unusual pattern? Does it swim vertically, horizontally, or in an unusual position? Does it struggle to maintain its position in the water column? A systematic observation of the fish’s swimming behavior and buoyancy can reveal subtle signs of the disorder.
Diagnostic Tests and Expected Results
| Diagnostic Test | Procedure | Expected Results (Swim Bladder Disorder) |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Observation | Carefully observe the fish’s swimming patterns, body posture, and overall behavior. Note any unusual movements or difficulty maintaining position. | Erratic swimming, difficulty maintaining buoyancy, tilting to one side, swimming in an unusual position, floating at the surface, or sinking to the bottom. |
| Water Quality Analysis | Measure ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, pH, and temperature levels in the aquarium water. | Elevated levels of ammonia, nitrite, or nitrate, or a pH outside the optimal range for the fish species. Unstable water parameters may contribute to the disorder. |
| X-ray | Take an X-ray of the fish to visualize the swim bladder. | An X-ray can reveal the presence of gas in the swim bladder or if it is collapsed or distorted. The X-ray may indicate inflammation or other issues affecting the swim bladder. |
| Ultrasound | Use ultrasound to assess the swim bladder and surrounding tissues. | An ultrasound can visualize the swim bladder’s size, shape, and contents, providing detailed information about its condition. It can also detect inflammation or other issues affecting the swim bladder. |
Treatment Methods
Swim bladder disorder, while often treatable, requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the specific fish and the severity of the condition. Proper diagnosis and assessment are crucial to determining the most effective course of action. A combination of therapeutic interventions, including medication, dietary adjustments, and supportive care, is frequently necessary for successful recovery.Effective treatment for swim bladder disorder necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the underlying cause and the fish’s overall health.
The following sections detail various treatment options, emphasizing the importance of individualised care plans.
Medication
Medication plays a crucial role in treating swim bladder disorder, particularly when an infection or underlying disease is suspected. Antibiotics, for example, may be prescribed to combat bacterial infections that could be contributing to the disorder. Anti-inflammatory medications might be used to reduce inflammation, easing discomfort and promoting healing. The choice of medication depends on the suspected cause and the fish’s overall health.
It’s imperative to follow veterinary recommendations precisely, including dosage and administration schedule, to ensure effectiveness and prevent potential side effects.
Dietary Changes
Dietary adjustments are often vital in managing swim bladder disorder. A diet tailored to the fish’s specific needs can aid in restoring its buoyancy. A balanced diet with appropriate protein levels is essential, while limiting excessive feeding is crucial to prevent overfeeding, which can exacerbate the condition. High-quality fish foods specifically formulated for fish with swim bladder issues can provide the necessary nutrients in an easily digestible form.
Supplementary Feeding
Supplementary feeding can be a valuable component of recovery, especially in cases of severe swim bladder disorder. In these instances, supplemental feeding can provide the necessary nutrients for growth and recovery. This is often used in conjunction with other treatments and should be implemented under the guidance of a veterinarian or experienced aquarist. The specific type and frequency of supplementary feeding will vary depending on the individual fish’s needs.
Maintaining Water Parameters
Maintaining optimal water parameters is paramount in treating swim bladder disorder. Clean, well-oxygenated water reduces stress and supports the fish’s overall health. Regular water changes, filtration, and monitoring of ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels are crucial to maintain a healthy environment for recovery. Fluctuations in water parameters can negatively impact the fish’s condition, therefore consistent monitoring and adjustments are necessary.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Medication (e.g., antibiotics, anti-inflammatories) | Generally effective when the disorder is caused by an infection or inflammation. | Possible allergic reactions, digestive upset, or interactions with other medications. |
| Dietary Changes (e.g., specific diets, portion control) | Effective in supporting recovery and preventing further complications from poor nutrition. | Potential for malnutrition if not implemented correctly. Requires careful monitoring of the fish’s appetite. |
| Supplementary Feeding | Can aid in recovery, especially in cases of severe disorder. | Potential for overfeeding if not managed properly. |
| Maintaining Water Parameters | Essential for creating a healthy environment conducive to recovery. | Improper water parameters can exacerbate the condition, causing stress and further illness. |
Environmental Considerations
Maintaining optimal water conditions is crucial for preventing and treating swim bladder disorder in fish. The environment plays a significant role in a fish’s ability to regulate buoyancy, and subtle changes can trigger or exacerbate the condition. Understanding the interplay between water quality, temperature, and chemistry is essential for effective management and recovery.Proper water parameters directly impact a fish’s ability to maintain buoyancy, impacting their overall health and well-being.
A healthy aquatic environment promotes a fish’s ability to maintain its natural buoyancy, minimizing the risk of swim bladder issues. Addressing environmental factors is often a critical component of successful treatment.
Water Quality
Water quality is paramount in preventing and treating swim bladder disorder. Contaminated water can stress fish, making them more susceptible to developing the condition. Regular water changes, appropriate filtration, and meticulous maintenance of the aquarium environment are essential for maintaining healthy water quality. Poor water quality often leads to increased ammonia and nitrite levels, which can compromise the fish’s immune system, increasing the risk of infection and complicating recovery from swim bladder disorder.
Water Temperature
Water temperature significantly influences a fish’s metabolic rate and buoyancy. Sudden or extreme temperature fluctuations can stress the fish, disrupting their internal balance and potentially triggering or worsening swim bladder disorder. Species-specific temperature ranges should be meticulously maintained to prevent such issues. Maintaining a stable and appropriate temperature range for the particular fish species is vital for successful treatment.
Water Chemistry
Water chemistry, including pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels, plays a critical role in a fish’s ability to maintain buoyancy. Imbalances in these parameters can lead to osmotic stress, affecting the fish’s internal fluid balance, thus impacting their ability to regulate buoyancy. Monitoring and adjusting water chemistry to maintain the specific requirements of the affected fish species is critical for recovery.
Ideal Water Parameters
The ideal water parameters vary significantly depending on the species of fish. Maintaining these parameters is crucial for the fish’s overall health and well-being. The following table provides a general guideline for ideal water parameters for some common fish species prone to swim bladder disorder. Note that these are general guidelines, and specific needs may vary.
| Fish Species | Temperature (°C) | pH | Ammonia (mg/L) | Nitrite (mg/L) | Nitrate (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goldfish | 22-24 | 7.0-7.5 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| Betta Fish | 24-28 | 6.5-7.5 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| Cichlids | 24-28 | 7.0-8.0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| Discus | 28-30 | 6.0-7.0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
Environmental Modifications for Recovery
Creating a supportive environment is critical for the fish’s recovery from swim bladder disorder. This involves gradual adjustments to the water parameters and a reduction in stress. Providing ample space and appropriate hiding places can reduce stress and allow the fish to rest and recover. Gradually reintroducing the fish to its original environment after treatment is essential.
Avoid sudden changes in the water parameters or environment that could further stress the fish. Monitoring the fish’s behavior and adjusting the environment as needed is critical.
Prevention and Management
Preventing swim bladder disorder in fish hinges on providing optimal environmental conditions and a healthy lifestyle. Proactive measures significantly reduce the risk of this debilitating condition, allowing fish to thrive and maintain their well-being. Careful attention to diet, stress reduction, and regular monitoring are crucial for successful prevention and management.Maintaining a healthy aquarium environment is paramount for preventing swim bladder disorder.
This involves not only the physical aspects of the tank but also the psychological well-being of the fish. By understanding the potential stressors and proactively mitigating them, aquarists can create an environment that fosters optimal health and reduces the risk of this condition.
Preventive Measures
A comprehensive approach to preventing swim bladder disorder necessitates a multifaceted strategy. Proper aquarium setup, including appropriate water parameters and filtration, is essential. Regular water changes, ensuring proper filtration, and maintaining stable water chemistry are crucial preventative measures.
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is vital for maintaining overall fish health and plays a significant role in preventing swim bladder disorder. A varied diet rich in essential nutrients, including proteins, vitamins, and minerals, is paramount. Overfeeding, on the other hand, can lead to various health problems, including swim bladder issues. Aquarium owners should avoid overfeeding and ensure their fish receive a nutritionally balanced diet that meets their specific needs.
This includes appropriate protein sources, and avoiding food that may cause digestive issues.
Stress Reduction
Stress is a significant contributing factor to many fish diseases, including swim bladder disorder. Identifying and mitigating stressors in the aquarium environment is critical. Factors like overcrowding, aggressive tank mates, sudden changes in water parameters, or inadequate hiding places can induce stress. Maintaining a peaceful and harmonious environment is paramount to minimizing stress and promoting the well-being of the fish.
Regular Monitoring
Regular observation and monitoring of fish behavior are crucial for early detection of swim bladder disorder. Changes in swimming patterns, appetite, or overall activity level can indicate underlying problems. This includes noting any changes in the fish’s swimming style, such as difficulty maintaining buoyancy or abnormal swimming patterns. Recognizing subtle signs of distress is essential for prompt intervention and treatment.
Preventative Checklist for Aquarium Owners
- Regular Water Changes: Consistently maintaining optimal water parameters, including temperature, pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels, is crucial for preventing stress and maintaining the health of the fish.
- Appropriate Filtration: A robust filtration system effectively removes waste products and maintains water quality, reducing the risk of water-borne diseases and stress.
- Balanced Diet: Offering a nutritionally complete and varied diet, tailored to the specific needs of the fish species, is essential for their overall health and helps prevent swim bladder issues.
- Stress-Free Environment: Avoiding overcrowding, ensuring suitable tank mates, and providing ample hiding places can significantly reduce stress and prevent swim bladder disorder.
- Regular Observation: Regularly observing the fish’s behavior for any changes in swimming patterns, appetite, or activity level is crucial for early detection of any potential health issues, including swim bladder disorder.
Case Studies and Examples
Understanding swim bladder disorder requires examining real-world examples of its progression, treatment, and outcomes. These case studies provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of different approaches and the factors influencing recovery or relapse. Analyzing diverse cases across various fish species allows for a broader understanding of the disorder’s complexity and variability.
Case Studies Demonstrating Treatment Effectiveness
Detailed case studies of swim bladder disorder in fish highlight the importance of accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans. These studies often track the progression of the condition, enabling researchers to assess the efficacy of specific interventions. For instance, studies on goldfish with swim bladder issues have demonstrated the positive impact of dietary adjustments rich in essential amino acids, leading to improved buoyancy and swimming ability.
Progression of Swim Bladder Disorder in Different Fish Species
The progression of swim bladder disorder varies depending on the fish species, their age, and overall health. Some species may exhibit a gradual deterioration of buoyancy, while others might experience acute episodes of instability. For example, in juvenile cichlids, the disorder may manifest as subtle deviations from normal swimming patterns, which can be easily overlooked. However, in older specimens, it might result in pronounced tilting or inability to maintain upright position.
These variations underscore the need for species-specific diagnostic approaches.
Examples of Successful Recovery from Swim Bladder Disorder
Successful recovery from swim bladder disorder showcases the positive impact of prompt and appropriate intervention. A common example involves a betta fish exhibiting impaired swimming due to swim bladder inflammation. By adjusting the water parameters, providing a balanced diet, and introducing appropriate medications, the fish displayed significant improvements in its swimming ability within a few weeks. This recovery demonstrated the importance of a multi-faceted approach to treatment.
Factors Contributing to Recovery or Relapse
Several factors can influence the outcome of swim bladder disorder treatment. Positive factors often include early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and maintenance of optimal water quality. Conversely, factors that contribute to relapse may include inadequate treatment, persistent poor water quality, or underlying health conditions. For instance, insufficient dietary protein in a patient goldfish could result in a recurrence of symptoms despite initial recovery.
Summary of Case Studies
| Fish Species | Treatment Methods | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Goldfish | Dietary adjustments (amino acid-rich diet), water quality improvement | Full recovery |
| Betta Fish | Water parameter adjustments, balanced diet, medications | Successful recovery within a few weeks |
| Juvenile Cichlids | Improved water parameters, monitoring for other potential health issues | Recovery, with continued monitoring |
Nutritional Support for Recovery

Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in the recovery of fish with swim bladder disorder. A balanced diet provides the essential nutrients needed to support the healing process, promote tissue repair, and strengthen the fish’s immune system, ultimately accelerating their return to good health. A targeted nutritional approach is often more effective than simply relying on standard fish food.Understanding the specific nutritional needs of affected fish is paramount.
This involves providing adequate protein and energy sources, as well as essential vitamins and minerals. The appropriate selection of high-quality fish foods can significantly impact the recovery rate. This section will delve into the vital role of specific nutrients in the healing process.
Protein and Energy Sources
Protein is essential for tissue repair and growth. Adequate protein intake is crucial for the repair of damaged tissues and the regeneration of healthy cells. Furthermore, energy sources are essential for the fish’s overall metabolic functions, especially during the recovery phase. Energy-rich foods provide the fuel necessary for tissue repair and immune function. This is especially important during the stressful period of recovery.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are vital components for maintaining overall health and supporting the immune system. Specific vitamins and minerals, like vitamin A, vitamin C, and various B vitamins, play critical roles in the body’s metabolic functions. Trace minerals such as zinc and copper are important for immune function. A deficiency in these nutrients can negatively impact the fish’s ability to fight off infections and accelerate recovery.
High-Quality Fish Foods
High-quality fish foods specifically formulated for disease recovery can be beneficial. These foods often contain a higher concentration of essential nutrients and a balanced ratio of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. They can also be fortified with specific vitamins and minerals tailored for recovery. Examples of these specialized foods include those containing readily digestible proteins, readily available energy sources, and optimal levels of essential nutrients.
Look for foods that clearly state their suitability for fish undergoing recovery.
Nutritional Strategies for Supporting the Immune System
Nutritional strategies for supporting a fish’s immune system during recovery should focus on foods rich in antioxidants. Antioxidants combat oxidative stress, which can hinder the recovery process. These strategies also involve providing foods with a balanced ratio of proteins and carbohydrates. In addition, ensure that the food is readily digestible and easily absorbed by the fish. For example, look for foods with a higher concentration of beta-carotene, which the body converts to vitamin A, crucial for immune function.
By supplying the proper nutrients, the fish’s immune system can effectively combat infection and promote healing.
Long-Term Care and Monitoring

A crucial aspect of successfully treating swim bladder disorder is long-term care and monitoring. This phase focuses on preventing recurrence, adapting the environment to the fish’s needs, and ensuring ongoing well-being. Proper long-term care contributes significantly to the fish’s recovery and long-term health.Sustained attention and appropriate adjustments to the environment and feeding practices are essential for a successful recovery.
This period requires proactive observation and meticulous attention to detail to identify and address potential issues early on.
Environmental Adaptation
Maintaining a stable and supportive environment is paramount during recovery. Changes in water parameters, such as temperature, pH, and ammonia levels, can trigger stress and potentially exacerbate the condition. Consistent monitoring and adjustments to maintain optimal conditions are essential.A well-maintained aquarium, equipped with proper filtration, aeration, and sufficient water circulation, will contribute to a stable environment. This also includes suitable water quality parameters, such as appropriate temperature, pH, and salinity (if applicable).
The tank’s layout should also be considered, ensuring adequate hiding places and areas for the fish to rest and recover. Avoid abrupt changes in water parameters, and maintain regular water changes to prevent the accumulation of harmful substances.
Feeding Strategies
Adjusting feeding strategies is a crucial component of long-term care. The fish’s digestive system may be compromised during recovery, so adjustments to the diet and feeding frequency are necessary. Introducing smaller, more frequent meals of high-quality, easily digestible foods is recommended.Small, high-quality food particles that are easily consumed and digested, like finely ground flakes or live foods, are often beneficial.
Overfeeding should be avoided as it can put additional strain on the digestive system. Observe the fish’s feeding habits closely, and adjust feeding amounts and frequency as needed. Consider supplementing the diet with nutritional supplements, as advised by a veterinarian specializing in aquatic animals.
Monitoring for Recurrence
Regular observation is essential for identifying early signs of recurrence. This includes careful attention to swimming patterns, appetite, and overall behavior. If any unusual signs emerge, immediate action is necessary. Consulting a veterinarian specializing in aquatic animals is advisable to ensure prompt diagnosis and treatment.Changes in swimming patterns, such as an inability to maintain buoyancy or exhibiting erratic swimming movements, should be monitored carefully.
Loss of appetite, lethargy, or changes in coloration can also indicate underlying issues that may need attention. Consistency in monitoring is crucial in identifying potential problems early.
Long-Term Care Checklist
- Regular Water Quality Monitoring: This includes checking temperature, pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels. Regular water changes are vital to maintain water quality.
- Consistent Feeding Schedule: Smaller, more frequent meals of high-quality, easily digestible foods are recommended. Observe the fish’s feeding habits and adjust as needed.
- Environmental Stability: Ensure a stable environment, with appropriate hiding places and areas for rest. Avoid abrupt changes in water parameters.
- Regular Observation: Monitor swimming patterns, appetite, and overall behavior. Look for any unusual signs, such as changes in coloration, lethargy, or erratic swimming movements.
- Professional Consultation: Consult with a veterinarian specializing in aquatic animals for guidance and advice if needed.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, treating swim bladder disorder requires a multifaceted approach that considers the fish’s specific needs, environmental factors, and nutritional requirements. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options Artikeld in this guide, you can equip yourself with the knowledge to effectively diagnose and manage this common fish ailment. Remember that early intervention is key to improving the chances of a successful recovery.